History
In 1992, researcher Dr. Raphael Mechoulam and his colleges we performing studies revolving around the structure and stereo chemistry of compounds within the Cannabis plant, particularly THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol), two of the 100+ phytocannabinoids located within the plant. While studying the effects of these phytocannbinoids on the human body, these researchers identified similar novel compounds within the body, which as he stated "were as potent as THC in binding to the receptor". These compounds were later identified as endocannbinoids: AEA (anandamide) and the chemically related 2-AG (2-arachidonoyl). Further research lead to the discovery of what we now know is the Endocannabinoid System located within the body.
The Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system composed of endocannabinoids, which are endogenous lipid-based neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors that are located throughout the body's central & peripheral nervous systems. Our body's endocannabinoid system is involved in the regulation of a variety of cognitive and physiological processes that include appetite, pain-sensation, mood, sleep and memory.
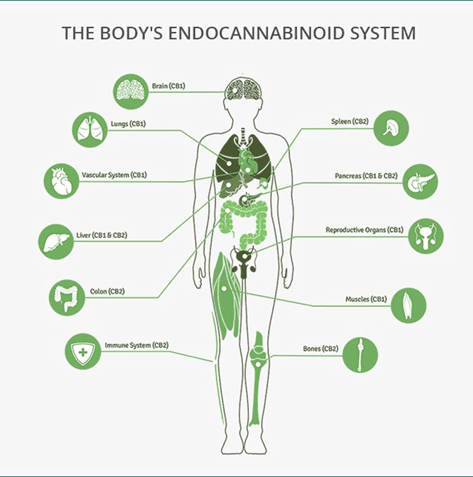
In the body, nerve cells also called neurons located throughout the body and brain are linked together by neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters are molecules that move from one neuron to another through the space between them, which it known as the synapse. As the neurotransmitters plug into neural receptors it causes a chain reaction. In the case of the endocannabinoid system, cannabinoids are the neurotransmitters that relay signals from one neuron to another. Two primary endocannabinoids receptors have been identified: cannabinoid-1 (CB1) and cannabinoid-2 (CB2). CB1 receptors are found in the highest concentration in the brain, but some are also present in the lungs, liver and kidneys. CB2 receptors are found throughout the body in the peripheral nervous system. It is interesting to note that there are more cannabinoid receptors in the brain than any other type of neural receptor. An easy way to think of it is that CB1 receptors are located mostly in the brain, while CB2 receptors are found throughout the body.
|
The endocannabinoid system is activated by naturally occurring "signaling molecules" called endocannabinoids produced by the body. The two primary endocannabinoids (endo meaning within or inside) in the human body have been label as anandamide (ananda a combination of the Sanskrit word meaning "bliss" and amide the chemical name for a part of the molecular structure) and 2-AG (2-archidonoyl glycerol). It is these two endocannabinoids that are synthesized and broken down in the body by five enzymes as follows: DAGL-a and DAGL-b (for synthesis of 2-AG), NAPE selective phospholipase-D (for synthesis of AEA), MAGL (for breakdown of 2-AG) and FAAH (for breakdown of AEA). AEA and 2-AG signaling molecules, regardless of location, activate both CB1 & CB2 receptor types.
New ongoing research has identified a complex interactional relationship between endocannabinoids and endorphins,hormones,cytokines,growth factors,gut health,pleasure molecules,immune cells,bone metabolism,cell regeneration,connective tissue systems,nerve and glial cell inflammation,and programmed cell death.
|
Endocannabinoid Systems Main Functions
Achieving Homeostasis
Our bodies are amazing and have a system built into us that monitors the body's constant struggle between building us up (anabolism) and breaking itself down (catabolism). When our bodies detect that we have gone too far in either direction, it works to balance us back to the middle, or better known as homeostasis. The endocannabinoid system is responsible for rebalancing the body and providing it with a constant and stable environment for which to function optimally. Bodies constantly make cannabinoids (endocannabinoids) to interact with its endocannabinoid system, ensuring that homeostasis continues. When your body is not in homeostasis, you are considered to be in a state of disease. This state of disease can impact almost every health conditions you can imagine. The endocannabinoid systems ability to rebalance allows the body's most essential systems to influence pain, mood, inflammation, energy, illness and wellness.
Due to the importance of this balance researchers Pacher and Kunos stated that "modulating Endocannabinoid system activity may have therapeutic potential in almost all diseases affecting humans, including obesity/metabolic syndrome, diabetes and diabetic complications, neurodegenerative, inflammatory, cardiovascular, liver, gastrointestinal, skin diseases, pain, psychiatric disorders, cachexia, cancer, chemotherapy inducted nausea and vomiting, around many others".
When not enough endocannainoids are created within the body, it is thought that Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency may occur. Recent research has noted that this condition may be treated by the introduction of hemp-based phytocannbinoids (THC, CBD). These two powerful phytocannabinoids act similar to the endcannabinoids, AGA and 2-AG, by influencing to the CB1 and CB2 receptors when introduced into the body.
Phytocannabinoids: CBD (cannabidiol) vs. THC (tetrahydrocannabinol)
CBD is one of the most abundant phytocannabinoids found in all varieties of the Cannabis plant, including hemp. It is a non-psychoactive plant compound, which means there is no mind altering effects from consumption and it will not cause positive results on drug tests. Research shows this compound stimulates the release of other endocannabinoids that activate both the CB1 and CB2 receptors producing a relaxing, body centric effect. It does this indirectly by suppressing the enzyme FAAH, responsible for the breakdown of AEA. CBD is thought to work with our own physical systems to inspire the body to achieve homeostasis.
THC on the other hand is the psychoactive compound that activates the CB1 receptors in the brain, and is responsible to the "high" associated with the hemp/ cannabis plant. It is mind altering at higher concentrations and consumption will give positive results on drug test. Our CBD Oil contains no detectable THC.
New Spirit Naturals CBD Multi-Complex Hemp Oil Concentrate
It seems that everyone from your grandparents to your neighbors are talking about CBD oil. The success stories are numerous about people taking responsibility for their own health. New research and studies are released daily that collaborate these success stories and the effects that Hemp oil containing CBD has on the bodies Endocannabinoid system and its ability to help achieve optimal wellness.
Natural Ways, New Spirit Naturals CBD Multi-Complex Hemp Oil Concentrate contains 300MG of naturally occurring CBD per bottle, which equates to approx. 10mg. per serving.
What Makes our CBD Muti-Complex Hemp Oil Concentrate Different?
Our hemp oil is cultivated in Oregon using organic practices with NO synthetic pesticides, NO fertilizers and NO chemicals of any kind in the growing process. Once the industrial hemp plants are harvested they are dried and processed in a large kiln. The hemp oil is then extracted using Carbon Dioxide CO2. The first pass of extraction is called the "crude" stage. This crude CBD oil is undergoes several rounds of distillation until the THC content is considered "non-detectable." The refinement process of the oil strips the impurities creating a pure and beautiful golden color oil. At this point the plants natural terpenes, the aromatic scent compounds are reintroduced to the oil. These terpenes amplify the beneficial effects of the oil in what is known as the "entourage effect." Our Hemp oil is label as Multi-Complex because it contains naturally occurring CBD phytocannabinoids along with other naturally occurring phytocannabinoids and terpenes contained in HEMP oil, but with no detectable THC. During the final state of the manufacturing process we synergistically combine the Hemp oil containing CBD with three other incredible ingredients: MCT Oil, Turmeric and Cinnamon Essentials oils.
- Tumeric
Used in India for thousands of years as a food and spice, this incredible herb has recently been hailed for its medicinal properties. Recent science has discovered that Turmeric contains compounds called curcuminoids, the most important of which is curcumin. This active in-gredient has been hailed for its powerful anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-aging effects.
- MCT Oil
MCT, or medium-chain triglycerides, a form of saturated fatty acids commonly derived from Coconut oil has numerous health benefits, ranging from improved cognitive function to better weight management. These MCT are largely missing from people consuming the "standard Western" diet because we have been lead to believe the saturated fats are potentially harmful. Recent evidence has shown that these MCT are easier to digest than long-chain triglycerides and support a healthy gut environment. MCT oil has high stability which makes it an ideal carrier of hemp and its abundance of phytocannabinoids.
- Cinnamon Essential Oil
Cinnamon has been revered by cultures around the world for centuries, as was once considered as value as gold. Cinnamon essential oil adds and incredible natural flavoring to the Hemp Oil Concentrate as well as a warm and soothing aroma that studies show has the ability to boost brain activity. Its increased popularity can be attributed to its anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, antimicrobial, astringent, and anti-inflammatory properties. Natural Cinnamon Essential oil provides the perfect flavoring compliment to this incredible product.
How To Use New Spirit Multi –Spectrum CBD Oil
Place one full dropper, 10mg (or approx. 35 drops) under the tongue and hold for 30-60 seconds. Store in a cool, dry place.
References
1-2. G.A Cabral, T.J. Rogers, and A.H. Lichtman, "Turning over a New Leaf: cannabinoid and Endocannabinoid Modulation of Immune Function" Jour-nal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology 10 (2015):193-203.
3-4. Dr. Michael Moskowitz. Bay Area Pain Medical Associates. Page 15-20. CBD, A Patient's Guide to Medicinal Cannabis, Healing without the High. Leonard Leinow and Juliana Birnbaum.
5. A.R Wilson-Poe, M.M. Morgan, S.A. Aicher, and D.M Hegarty, "Distribution of CB1 canabinoid Receptors and their relationship with Mu-opiod Re-ceptors in the Rat Periaqueductal Gray" , Neurosceince 213 (2012): 191-200.
6. T. Lowin and R.H straub, "Cannabinoid Based Drugs Targeting CB1 and TRVP-1, the Sympathic Nervous System and Arthritis," Arthritis Reasearch and Theraphy 17 (2015):226.
7. A.E Bonnett and Y. Marchalant, "Potential Therapeutic Contribution of the Endocannabinoid System towards Againg and Alzheimer's Disease," Aging and Disease 6, no. 5 (Oct 2015): 400-405
8. M. Fitzgibbon, D. P. Finn, and M Roche, "High Times for Pain Blues: The Endocannbinoid System in Pain-Depression Co-morbidity," Interna-tionalJournal of Neuropharmacology (2015): 1-20.
9. K.A. Sharkey and J.W. Wiley, "The Role of the Endocannabinoid System in the Brain-Gut Axis," Gastroenterology 151, no @ (2016): 252, doi:10, 1053/j.gastro. 2016.04.015.
10. S.V Mahler, K.S. Smith, and K.C Berridge, "Endocannabinoid Hedonic Hotspots for Sensory Pleasure: Anandamide in the Nucleus Accumbens, Shell Enhances Liking of a Sweat Reward," Neuropharmacology 32 (2007): 2267-2278.
11. P. Pacher an R. Mechoulam, "Is Lipid Signaling through Cannabinoid 2 receptors part of a protective system"? Progress in Lipid research (April 2011): 193-211.
12. R.G Pertwee, A.C Howlett, M.E Abood "International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmcology, LXXIX: Cannabinoid Receptors and Their Ligands, Beyond CB1 and CB2," Pharmacologic Reviews 62, no. 4 92010): 588-631.
13. E. Shohami, A Cohen-Yeshurun, L. Magid "Endocannabinoids and Traumatic Brain Injury," British Journal of Pharmacology 163, no. 7 (august 2011): 1402-1410.
14. N.M Kogan, E. Melamed, E. Wasserman, B. Raphael. "Cannabidiol, A Major Non-psychotropic Cannabis Constituent, Enhances Fracture Healing and Stimulates Lysyl Hydroxylase Activity in Osteoblast." Journal of Mineral and Bone Research 30, no. 10 (Oct 2015): 1905-1913.
15. Antonio Currais, Oswald Quehenberger, Aaron Armando, Pam Maher, and Daid Schubert, " Amyloid Proteotoxicity Initiates an Inflammatory Re-sponse Blocked by Cannabinoids," Nature Partner Journals: Aging and Mechanism of Disease 2, no. 16012 (June 23, 2016) doi: 10.1038.
16. Rocio Snacho, Marco Calzado, Vincenzo Di Marzo, Giovanni Appendino, and Eduardo Munoz, "Anandamide Inhibits Nuclear Factor K-beta Activia-tion through a Cannabinoid Receptor Independent Pathway." Molecular Pharmacology 63, no. 2 (2003): 429-438.
17. P. Pacher and G Kunos, "Modulating the Endconnabinoid System in Human Health and Disease: Sucessses and Failures," Federation of European Biochemical Society Journal 280, no 9 (May 2013): 1918.
18. Chainani-Wu N, Safety and anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin: A component of turmeric (Curcuma longa). J Altern complement Medicine (Feb 2003) ; 9 (1): 161-8.
19. Menon VP, Sudheer AR. "Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of Curcumin." Advance Exp. Medical Biology 2007: 595:105-25.
20. Sikora E, Scapagnini G. Barbagalio M. "Curcumin, inflammation, ageing and age-related diseases." Immun Ageing 2010 Jan 17: 7(1):1 doi 10. 1186/1742-4933-7-1.
21. Schonfeld P, Wojtczak L. " Short and medium-chain fatty acids in energy metabolism: the cellular perspective" J lipid Res 2016 Jun: 57 (6): 943-54. Doi: 10:1194/jlr R067629 Epub 2016 Apr 14.
22.St-Onge MP, Jones P. "Greater rise in fat oxidation with medium-chain trigycerides consumption to long-chain triglycerides is associated with lower initial body weight and greater loss of subcutaneous adipose tissue. " Int Journal Rleate Metabolic Disorders 2003 Dec: 27 (12): 1565-71.
23 Dr. P. Zoladz, Wheeling Jesuit University. Research on Cinnamon's ability ot improve cognitive activities such as attention span, virtual recognition memory, working memory, and visual motor speed.
24. Gunawardena D, Karunaweera N., Lee S. Munch G. "Anti-inflammatory activity of cinnamon extracts- identification of E-cinnamaldehyde and o-methoxy cinnamaldehyde as the most potent bioactive compounds." Food Function 2015 Mar : 6 (3): 910-9. Doi: 10 1039/c4fo00680a.


